Comparing Alexis and Endo Catch Systems for Specimen Removal in Laparoscopic Procedures: Benefits and Considerations
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that has become the standard for many surgical interventions. One of the critical aspects of laparoscopic surgery is the ability to remove the specimen from the patient's body without causing significant tissue damage. Two devices that are commonly used for specimen removal in laparoscopic surgery are the Alexis and Endocatch devices. In this article, we will compare these two devices and explore their respective pros and cons.
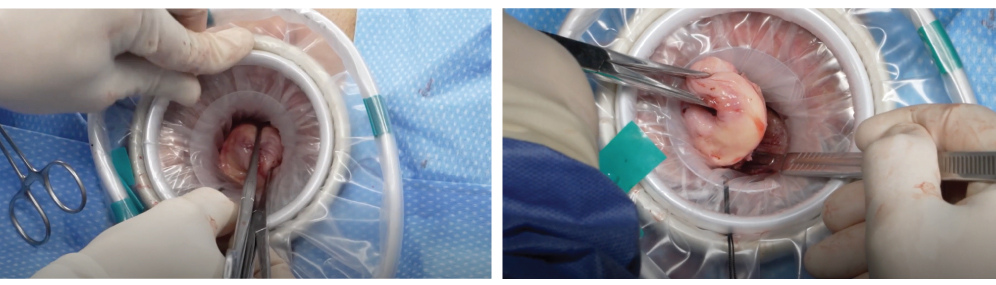
Alexis Device: The Alexis device is a wound protector and retractor that is designed to provide a large working space while reducing tissue trauma. The device consists of a balloon-like sleeve that is inserted through the incision site and inflated to create a protective barrier around the surgical site. The Alexis device is ideal for procedures that require the removal of large specimens and is commonly used in urologic and gynecologic surgeries.
Pros:
Large working space: The Alexis device creates a large working space, making it easy for the surgeon to manipulate the instruments and remove the specimen.
Reduced tissue trauma: The balloon-like sleeve of the Alexis device protects the surrounding tissue, reducing the risk of tissue trauma.
Easy to use: The Alexis device is easy to use and can be quickly inserted and inflated, making it an ideal choice for procedures that require rapid specimen removal.
Cons:
Expensive: The Alexis device is more expensive than other specimen removal devices, which can make it less accessible for some healthcare facilities.
Bulky: The size of the Alexis device can make it challenging to use in small incision sites, making it unsuitable for certain procedures.
Endocatch Device: The Endocatch device is a specimen retrieval bag that is designed to capture and remove the specimen from the body. The device is made of a flexible mesh material that allows it to conform to the shape of the specimen. The Endocatch device is commonly used in a variety of laparoscopic procedures, including cholecystectomy, appendectomy, and gastric bypass surgery.
Pros:
Low cost: The Endocatch device is less expensive than the Alexis device, making it a more cost-effective option for healthcare facilities.
Easy to use: The Endocatch device is easy to use and can be quickly inserted and opened, making it an ideal choice for procedures that require rapid specimen removal.
Versatile: The Endocatch device can be used in a variety of laparoscopic procedures, making it a versatile tool for healthcare providers.
Cons:
Limited working space: The Endocatch device can provide limited working space, making it challenging to manipulate instruments and remove larger specimens.
Risk of specimen rupture: The Endocatch device can rupture if too much force is used during specimen removal, which can result in the loss of the specimen and potential complications for the patient.
In conclusion, both the Alexis and Endocatch devices have their respective pros and cons when it comes to specimen removal in laparoscopic surgery. The Alexis device provides a larger working space and reduces tissue trauma, making it an ideal choice for procedures that require the removal of larger specimens. On the other hand, the Endocatch device is a more cost-effective option and is versatile enough to be used in a variety of laparoscopic procedures. Ultimately, the choice of device will depend on the specific needs of the patient and the preferences of the surgeon.










Comments
Post a Comment